[ Newlines Mag ] The Taliban’s Struggle to Control Kabul
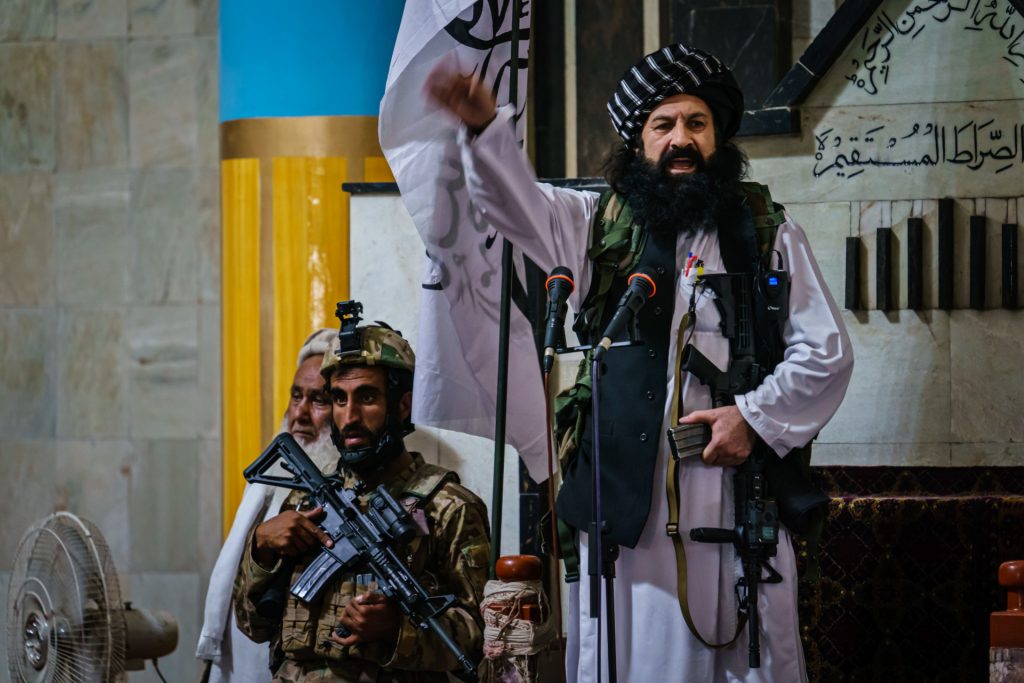

Before formally entering Kabul, the Taliban had already secreted men into the city, where they were biding their time, ready to take over the capital. But the quick collapse of the capital caught even them unprepared. The units assigned to secure the city were still busy clearing the outskirts of the capital and neighboring provinces when they were ordered to Kabul. They arrived in smaller numbers, exhausted and fatigued, immediately tasked with overseeing a large and chaotic city.
Under the direct control of its political office in Doha, the Taliban dispatched a newly formed military unit to guard the Parliament, its members, houses of political leaders and high officials of the former government.
The emir who issued the order by phone told him, “The Doha office is in touch with him [Rahmani], so don’t do anything wrong.” The commander had grown up in a neighboring province and wasn’t familiar with Kabul so had no idea where Rahmani’s house was. In a ranger truck seized from police, he traversed the city with three young Taliban to the speaker’s house in the north of Kabul, which turned out to be a castle located on the side of the main road. After a brief skirmish with a unit of the Afghan National Security Directorate, they were able to take control of Rahmani’s home.
Other units of the quick reaction force were dispatched to secure the Green Zone, central bank, private banks and money exchange markets. But the immediate fall of Kabul caught them unprepared.
Unrulier elements of the Taliban, from the provinces neighboring Kabul, entered the capital creating mayhem, since few had an idea of what was required of them. “Some of the groups are stronger than the governor of Taliban,” said the commander. These include men under the command of Khalil al-Rahman Haqqani, who, according to Western press, have been put in charge of Kabul’s security. However, there has been no such official authorization from the Taliban’s central command.
The Taliban divided Kabul into three security zones, each with several police districts. In only one of the zones, groups from Khost and Paktia, the Haqqani heartlands, control about half of the police stations. These groups do not act independently of the Taliban but report to the governor. According to Taliban sources, Haqqani is in Kabul as a tribal and religious elder rather than as an official sent by the Taliban.
Many Red Units — the elite Taliban forces created in each province — and strong military factions, such as Fateh Zwak, are likewise stationed in Kabul without the authorization of the leadership. This has weakened discipline, and the leadership is struggling to assert control.
The Taliban had no capacity to check all the vehicles, and the threat of sectarian attacks by the Islamic State group remains high.
The Taliban deputy leader arrived in Kandahar, and some of the political office members were already in Kabul to advance talks about the political transition in the country. “The Taliban could announce the restoration of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, but our leaders are proceeding with talks aimed at forming an open inclusive Islamic government,” said the Taliban official.
The Taliban intend to form a council that includes Karzai, Hekmatyar and former presidential candidate Abdullah in the interim government, which will be led by the supreme leader of the Taliban Sheikh Haibatullah.
“In the forthcoming government, strong parties will have seats, like Hezb-e-Islami; Jamiat-e-Islami (Abdullah’s faction); and Khalil’s Wahdat-e-Islami faction,” said the official. He mentioned that there was pressure from Qatar and Pakistan to include Karzai or Abdullah as deputies in the new interim ruling council. In Kabul, they have allowed Mayor Mohammad Daoud Sultanzoy to continue in office, though under the supervision of a Taliban commission.
In the coming weeks, as the Taliban try to form a new government, they will have to find ways to reconcile the competing interests of the different factions they are trying to court to give their rule legitimacy. It remains to be seen, however, if they have the capacity to enforce discipline within their own ranks.