[ NPR ] Guinea’s Military Declared A Coup. What Happens Next Is Uncertain
One day after the military stormed the president of Guinea’s palace and took him into custody, the coup’s leader ordered ministers from the ousted government not to depart the country and to hand over their official vehicles.
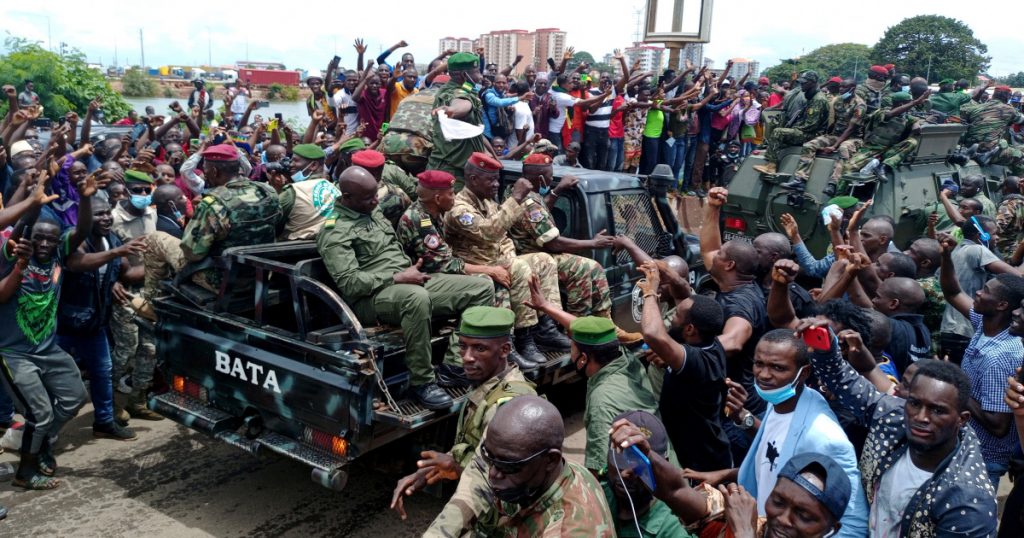

The coup began Sunday with reports of heavy gunfire near the presidential palace in Conakry, the country’s capital. At first, Guinea’s Defense Ministry said the incursion had been quashed. But photos soon emerged of the president, 83-year-old Alpha Conde, in captivity, surrounded by men in military fatigues.
Col. Doumbouya, a 41-year-old former member of the French legionary, appeared on state television Sunday to announce that the country’s government and constitution had been dissolved and a new government would be formed soon, though he did not provide a timeline. He said he led the coup to end the president’s corrupt administration, which had failed to bring economic prosperity to the country.
“We will no longer entrust politics to one man. We will entrust it to the people,” Doumbouya said.
The coup was met with widespread condemnation on Sunday. U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres tweeted that he was “personally following the situation in Guinea very closely,” and called for the military to release the deposed president.

President Conde’s capture comes less than a year after a violently contested election that led to the start of his third term, according to the Associated Press. In 2020 Conde rammed through a referendum to change the constitution, which then allowed him to run for a third term.
On Sunday many took to the streets to celebrate Conde’s removal from power, running and cheering alongside passing military vehicles.
Alpha Conde ascended to his role as the country’s leader in 2010 as Guinea’s first democratically elected president. His government helped boost mining and exports of its vast quantities of the mineral bauxite, used in the manufacturing of aluminum. But, as Human Rights Watch documented in 2018, the bauxite operations disrupted the lives and livelihoods of many in rural Guinea. Frustration had also been mounting over the years that the wealth gained from bauxite was not trickling down to most of the country.