POLAND WILL NO LONGER ARM UKRAINE, after Ukraine complains to WTO over grain ban in Poland
In a series of recent developments, tensions have flared between Ukraine and several European Union member states, leading to significant economic and political repercussions.
On September 15th, the European Commission announced the termination of the import ban on grain from Ukraine. This decision marked the culmination of a previous agreement made in May by the European Union to impose restrictions on the import of Ukrainian grain, confining it to Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Slovakia. The primary objective of these measures was to protect local farmers in these nations who attributed declining prices on their domestic markets to the inundation of Ukrainian grain. While the restrictions allowed Ukraine to transit its products through these five countries, they effectively prohibited their sale on local markets.
The European Commission justified its decision to end the import ban by citing the disappearance of market distortions in the five member states bordering Ukraine. Nevertheless, Poland, Hungary, and Slovakia immediately contested the move, sparking controversy, especially in Poland, where elections were impending.
Subsequently, on September 19th, Ukraine filed a formal complaint with the World Trade Organization (WTO) against Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. This complaint was lodged in response to these countries imposing bans on the import of grain and other food products from Ukraine. Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal made the announcement, highlighting the ongoing discord within the agricultural sector and further deepening the rift between Ukraine—a major global food supplier—and three European Union member states. The EU has been a crucial supporter of Ukraine as it grapples with Russia’s invasion.
In a divergence from the broader EU stance, Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, and Croatia (the latter joining later) implemented bans on Ukrainian food imports into their local markets. However, they decided to continue permitting these products to transit through their borders to regions where there was a demand for food. These decisions were prompted by the EU’s recent decision to lift restrictions on Ukrainian exports to five member states, including Romania and Bulgaria. Notably, Bulgaria’s government chose to reinstate Ukrainian imports, citing the surge in food costs, which had triggered farmer protests.
Croatian Prime Minister Andrej Plenkovic echoed the concerns of the other nations, expressing fears that importing cheaper Ukrainian grain could adversely affect local farmers. Nevertheless, Croatia extended an olive branch by offering its Adriatic Sea ports to facilitate the export of Ukrainian grain to other countries. In response, Ukraine’s Prime Minister criticized these actions as “unfriendly” and launched an investigation into potential discriminatory practices.

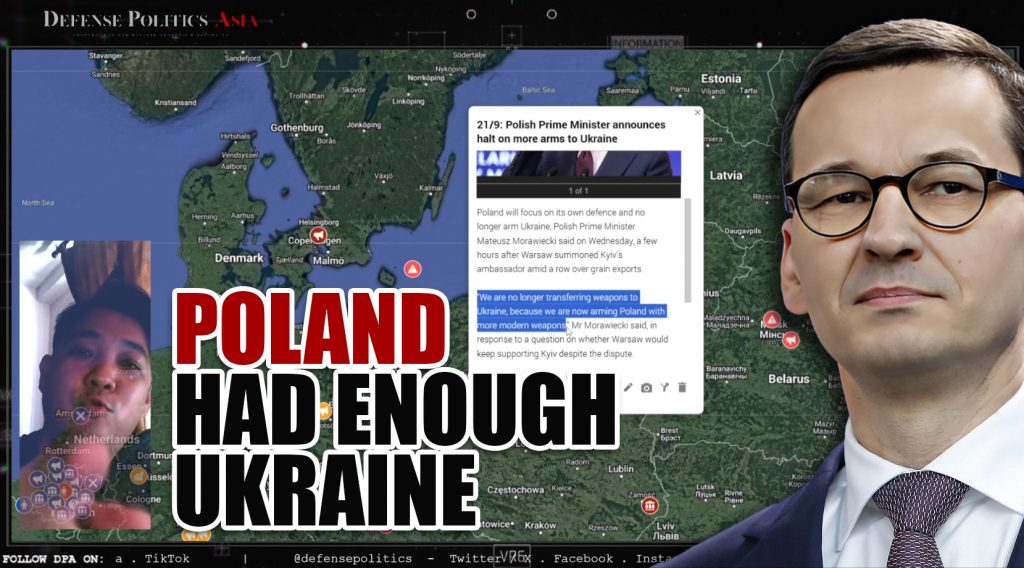
Finally, on September 21st, Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki unveiled a policy shift concerning arms supplies to Ukraine. He declared that Poland would focus on strengthening its own defense capabilities and cease arming Ukraine. This decision followed the summoning of Kyiv’s ambassador by Warsaw amid the ongoing dispute over grain exports.
Poland, a major supplier of weapons to Ukraine and a steadfast supporter since Russia’s invasion in February 2022, has also provided assistance to approximately one million Ukrainian refugees. The decision to halt arms transfers to Ukraine underscores Poland’s changing priorities, emphasizing the modernization of its own defense capabilities. These interconnected developments exemplify the intricate web of economic, political, and security interests at play in the region.
FULL REPORT & ANALYSIS: