[ TIME ] China, Isolated From the World, Is Now the Last Major Country Still Pursuing a ‘Zero COVID’ Strategy
Now, with the rise of the delta variant and the proliferation of vaccines, only one is still holding fast to that goal of eliminating Covid-19: China.
With New Zealand preparing to shift away from the zero-tolerance strategy, China’s isolation is complete, raising the stakes on how long it can stick to a playbook that requires closed borders, abrupt lockdowns, and repeated disruption of social and economic activity.
One by one, Covid Zero places like Singapore and Australia have decided that the approach is unsustainable, pivoting instead to vaccination to protect people from serious illness and death while easing off on attempts to control the number of infections.
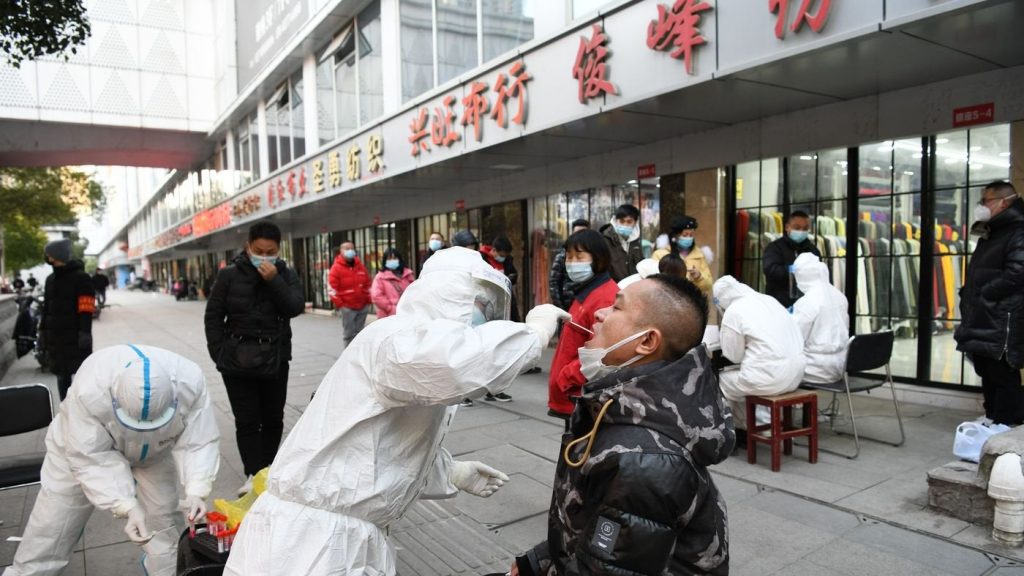

Photo: VCG/VCG via Getty Images
In contrast, China’s resolve to stamp out every infection appears to have only grown stronger, though 75% of its vast population is fully vaccinated. The country is now grappling with its fourth delta-driven flareup in two months and this week locked down a prefecture in the western Xinjiang province over two asymptomatic infections during a peak tourism period.
The Chinese territory of Hong Kong, which has so far avoided local transmission of delta, has also made clear that its status as a global financial hub is less important than links to the mainland and the joint goal of elimination.
The task is likely to get even harder as cold weather — the conditions in which the virus spreads best — descends. In three months, Beijing will host the Winter Olympics, welcoming thousands of athletes from around the world.

Still, the status has become a political point of pride for China, with authorities trumpeting their success in containing the virus as an ideological and moral victory over the U.S. and other nations now treating the virus as endemic.
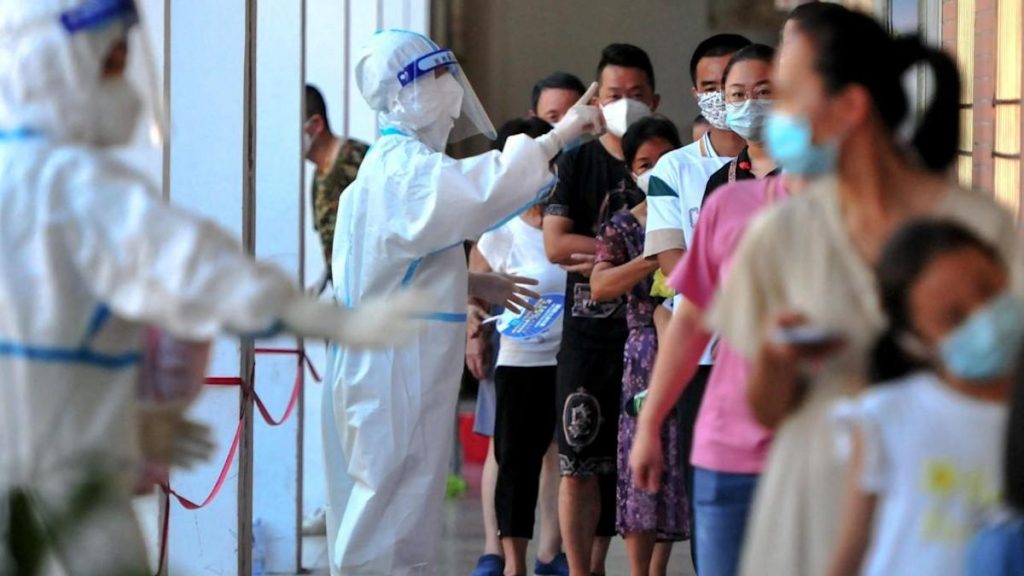

Officials in China have said they won’t stick to Covid Zero forever, though it will only consider a change when the approach no longer works or the costs are too high — parameters of which have not been made public. City governments are being asked to create specialized quarantine facilities that could house thousands of overseas arrivals by the end of October, signaling that onerous travel curbs are unlikely to be eased in the near term.
Achieving elimination allowed life in China to be largely normal through most of 2020 and 2021, powering its economy even as most others were sapped by mitigation measures of various efficacy. But as its snap lockdowns and restrictions on movement continue through this year — and western economies resume full operations after vaccination — the impact is starting to show more deeply. Retail sales growth slowed to 2.5% in August from a year earlier, falling far short of the 7% expansion estimated by analysts.